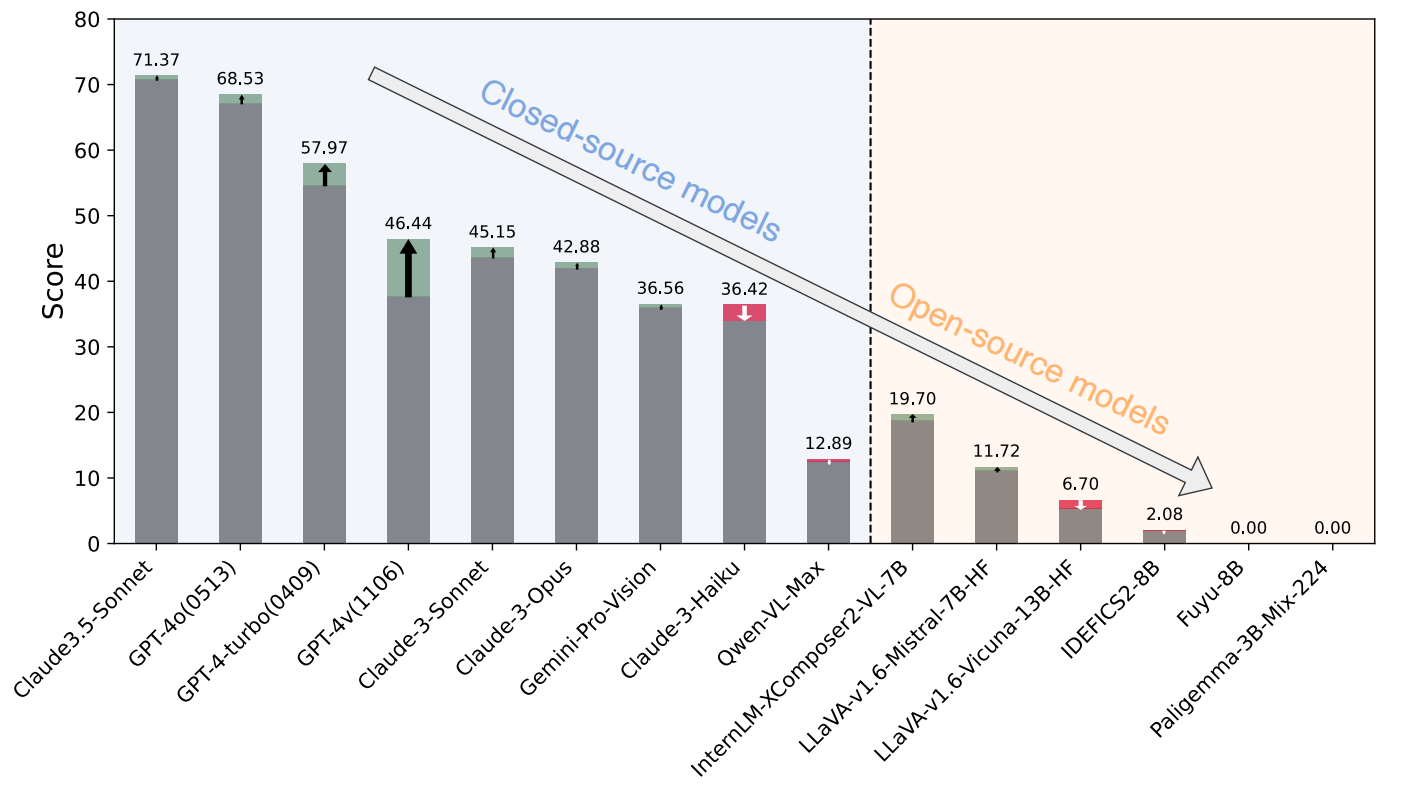
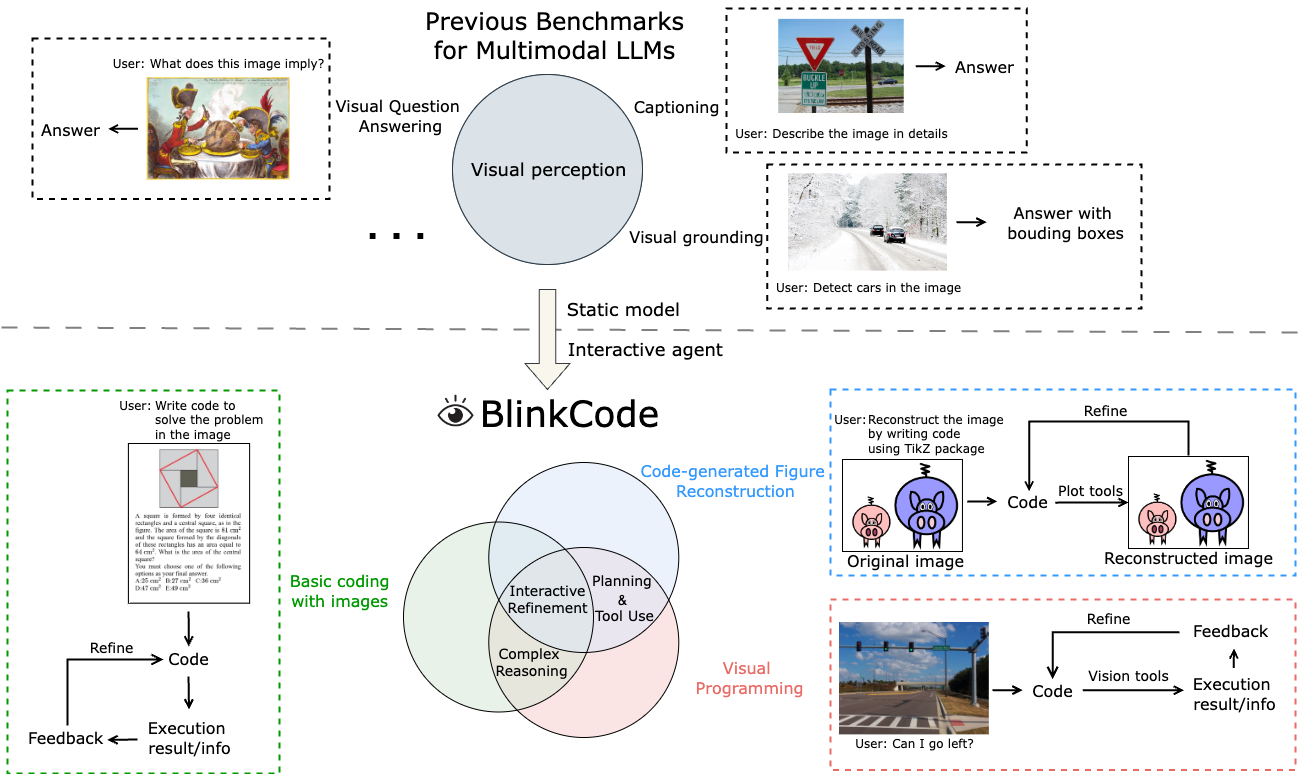
Program synthesis is a critical capability of Large Language Models (LLMs). The generated code is often used as an interface for LLMs to act as agents and interact with the environment. On the other hand, multimodal LLMs, equipped with additional vision modules, have the potential to act as vision-enabled agents that perform interactive tasks with perceived visual information. It is thus also important for multimodal LLMs to be able to generate executable code, yet based on what they have observed in the environment. While well-designed interactive coding benchmarks have been proposed for LLMs, appropriate ones for multimodal LLMs are lacking. We thus propose BlinkCode, an interactive, comprehensive, visual coding benchmark with execution feedback for multimodal LLMs. BlinkCode covers three types of tasks, evaluating capabilities including basic coding, planning, and refinement based on visual information. Our evaluation result demonstrates that, as opposed to LLMs, most open-source multimodal LLMs lack coding capabilities, calling for the community to develop techniques to inject coding skills into multimodal LLMs to turn them into vision-enabled agents. We include the whole dataset in the supplementary material.